

Valuing Water | Transforming Ganga
Twin Summits
10th India Water Impact Summit
[IWIS]
From Segmented Efforts to Holistic Stewardship:
Forging District River Management Plans for India's Water Future
&
3rd Climate Investments and Technology Impact Summit
[CITIS]
Grounding Climate Investment and Technology Innovation at
District Level in India
December 9-11, 2025
Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, New Delhi

National River Conservation Directorate [NRCD]
Condition Assessment and Management Plan [CAMP]
Command Centre at cGanga, IIT Kanpur
About the Summits
The Center for Ganga River Basin Management and Studies (cGanga) is pleased to organize the 10th India Water Impact Summit [IWIS] & 3rd Climate Investments and Technology Impact Summit [CITIS] during 9 – 11 December 2025. The Summits will be held at Indian Institute of Technology Delhi.
Restoration and Conservation of
Small Rivers in a Large Basin
8th India Water Impact Summit [IWIS 2023]
“Mapping and Convergence of 5Ps”
(People, Policies, Plans, Programmes & Projects)
Glimpses of 1st to 9th India Water Impact Summit

Themes of 1st to 9th India Water Impact Summit

IWIS 2025 | From Segmented Efforts to Holistic Stewardship Forging District River Management Plans for India's Water Future


Figure 1: Representation of River Rejuvenation and Conservation Efficacy as an Interplay Amongst Several Aspects
इंडिया वॉटर इम्पैक्ट समिट 2024
इंडिया वॉटर इम्पैक्ट समिट का प्रारंभ वर्ष 2012 में आईआईटी की सात संस्थानों के संघ द्वारा द्वारा गंगा रिवर बेसिन मैनेजमेंट प्लान विकसित करने के दौरान नदी बेसिन प्रबंधन के विषय में विभिन्न वैज्ञानिक, तकनीकी, सामाजिक- सांस्कृतिक, नीतिगत, कानूनी और प्रशासनिक विषयों पर स्पष्टता लाने के उद्देश्य से किया गया था। नदी बेसिन प्रबंधन के संदर्भ में देखा जाए तो असंख्य विविधताओं से भरे देश में विभिन्न हितधारकों के हित, रूझान और नदी की प्रक्रियाओं से जुड़ी समझ और दृष्टिकोण भी विविधतापूर्ण है। वर्ष 2015 में गंगा रिवर बेसिन मैनेजमेंट प्लान (जीआरबीएमपी) तैयार होने के बाद उपरोक्त विषयों पर अधिक स्पष्टता लाने के लिए छह वर्षों में प्रतिवर्ष शिखर सम्मेलन आयोजित किये गए। जिनका उद्देश्य था, नदी बेसिन प्रबंधन से संबंधित कुछ अस्पष्ट और विवादास्पद विषयों पर आपसी विमर्श और विश्लेषण के द्वारा वैज्ञानिक समझ और सर्वसम्मति विकसित करना। इसके साथ ही इन सम्मेलनों में बेसिन प्रबंधन के विश्लेषणात्मक उपकरण, डाटा संबंधी आवश्यकताओं की पूर्ति, निगरानी तंत्र और योजनाओं के क्रियान्वयन और नीतिगत मुद्दों पर सरकारी और निजी स्तर पर जारी प्रयासों और हितधारकों के बीच बेहतर समन्वय स्थापित करने के तरीकों पर चर्चा हुई। तकनीक और नवीन अविष्कारों का उपयोग करते हुए भारत के समग्र जलीय पर्यावरण का बेहतर प्रबंधन करने पर गहन मंथन हुआ।
इंडिया वॉटर इम्पैक्ट समिट आज एक बहुप्रतीक्षित शिखर सम्मेलन है। जिसमें विषय विशेषज्ञ, शासकीय प्रतिनिधि, हितधारकों के प्रतिनिधि एक मंच पर नदी घाटी प्रबंधन और जलप्रबंधन के समक्ष खड़ी चुनौतियों और समाधान के नए विकल्पों पर विमर्श करते हैं। सम्मेलन के दौरान अलग-अलग सत्रों में वैज्ञानिक, तकनीकी और नीतिगत विषयों पर विचार-मंथन होता है, साथ ही केंद्र और राज्य सरकारों के प्रतिनिधि विभिन्न विषयों पर शासन के दृष्टिकोण को स्पष्ट करते हैं। इन सत्रों में नवीन तकनीकों की समीक्षा करने के साथ, निवेशक और तकनीकी प्रदाता के हितों को समन्वित करते हुए विभिन्न पहलूओं की पड़ताल की जाती है ताकि भारत में जलप्रबंधन के क्षेत्र में तकनीक आधारित जलप्रबंधन की सुदृढ़ संस्कृति विकसित की जा सके।
इन प्रयासों के मध्य जलवायु परिवर्तन और उसके परिणामों को देखते हुए जल और पर्यावरण क्षेत्र में नवीन तकनीकों, नए आविष्कारों को सम्मिलित करने की आवश्यकता अब अनिवार्यता बन गई है। यही कारण है कि वर्ष 2023 से शिखर सम्मेलन द्विआयामी हो गया है। सम्मेलन के दो आयाम होते हैं – द इंडिया वॉटर इम्पैक्ट समिट (IWIS) और क्लाइमेट इन्वेस्टमेंट एंड टेक्नोलॉजी इम्पैक्ट समिट (CITIS)। शिखर सम्मेलन के दूसरे आयाम का उद्देश्य समीक्षा और परीक्षण के बाद प्रौद्योगिकी प्रदाताओं और संभावित निवेशकों को साथ जोड़ना है। इंडिया वॉटर इम्पैक्ट समिट के सहआयोजन में वैज्ञानिक समीक्षा में खरी उतरी तकनीकों के क्रियान्वयन, नई तकनीकों के लिए वित्तपोषण की विधियों और व्यवसाय के नए मॉडल्स जैसे विषयों पर समन्वित चर्चाएँ होंगी । जिससे इन तकनीकों का समावेश भविष्य में ऊर्जा, कृषि, शहरी विकास, परिवहन, अधोसंरचना विकास जैसे क्षेत्रों में किया जा सके क्योंकि यह सभी क्षेत्र पर्यावरण, जल, वायु, भूमि, नदियों और जल प्रबंधन से गहनता से अंतर्संबंधित हैं।
नौवीं इंडिया वॉटर इम्पैक्ट समिट में पिछले सत्रों की उपलब्धियों पर आधारित एक प्रदर्शनी लगाई जाएगी। साथ ही विगत वर्षों में नदी पुनर्जीवन और संरक्षण के लिए जमीनी स्तर पर क्रियान्वित की गई योजनाओं, परियोजनाओं, कार्यक्रमों और परियोजनाओं से प्राप्त अनुभवों पर विशेषज्ञों का विमर्श होगा और भविष्य की रणनीति तय की जाएगी।
भारत में नदी को स्वच्छ बनाने के लिए सम्मिलित प्रयासों की शुरूआत वर्ष 1985 में गंगा एक्शन प्लान के साथ हो गई थी। इन्ही प्रयासों को विस्तार देते हुए यमुना एक्शन प्लान भी बनाया गया। उसके बाद ऐसे ही प्रयास अन्य नदियों के लिए भी नेशनल रिवर कन्जर्वेशन प्लान (एनआरसीपी ) के तहत किये गए।
गंगा एक्शन प्लान, यमुना एक्शन प्लान और नेशनल रिवर कन्जर्वेशन प्लान की विस्तृत समीक्षा के बाद सात आईआईटी (इंडियन इंस्टीट्यूट ऑफ टेक्नोलॉजी) के संघ द्वारा वर्ष 2015 में गंगा रिवर बेसिन मैनजमेंट प्लान प्रस्तुत किया गया, जिसका मुख्य उद्देश्य गंगा नदी को गंगा की संपूर्णता के साथ सहेजना था। जीआरबीएमपी (गंगा रिवर बेसिन मैनेजमेंट प्लान) में सुझाए गए कुछ बिंदुओं ने नदी पुनर्जीवन और संरक्षण के उद्देश्य से प्रारंभ किये गए नमामी गंगे कार्यक्रम के लिए मजबूत आधार तैयार किया।
नमामी गंगे के प्रारंभ में ही यह महसूस हुआ की जीआरबीएमपी के क्रियान्वयन के लिए विशेषज्ञों के मार्गदर्शन की आवश्यकता होगी साथ ही यह भी महसूस हुआ कि इस योजना की सफलता और इसकी गति, समय-समय पर योजना के मूल्यांकन, पुनर्मूल्यांकन और पुनर्विकास पर निर्भर करेगी। इसी उद्देश्य की पूर्ति के लिए आईआईटी कानपुर के नेतृत्व में सेंटर फॉर गंगा रिवर बेसिन मैनेजमेंट एंड स्टडीज जिसे सी-गंगा के नाम से जाना जाता है, की स्थापना हुई। कई राष्ट्रीय महत्व के शैक्षणिक संस्थान जैसे आईआईटी, एनआईटी, आईआईएसईआर सी-गंगा के सदस्य संस्थान हैं, साथ ही सी-गंगा की विभिन्न परियोजना में भागीदार भी हैं। नेशनल मिशन फॅार क्लीन गंगा के सहयोग से सी-गंगा ना केवल राष्ट्रीय बल्कि अंतर्राष्ट्रीय संस्थानों के साथ भी साझेदारी में विभिन्न परियोजना में सक्रिय है। गौरतलब है कि एनएमसीजी (नेशनल मिशन फॉर क्लीन गंगा अथवा स्वच्छ गंगा मिशन), नमामी गंगे कार्यक्रम की प्रमुख कार्यकारी संस्था है।
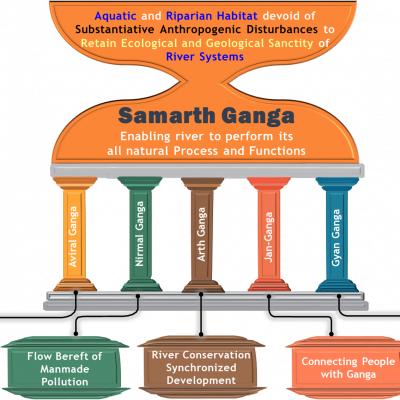
नदी पुनर्जीवन और संरक्षण के विभिन्न पहलू परस्पर अंतर्संबंधित हैं, जिन्हे चित्र क्रमांक एक में दिखाया गया है। जिसमें शामिल हैं – 1. उद्देश्य का निर्धारण, 2. रिवर बेसिन मैनेजमेंट प्लान और उसका ढांचा, 3. जमीनी स्तर पर कार्यवाही के लिए विज्ञान, तकनीक, नीति, कानून, प्रशासन, वित्त पोषण और जनभागीदारी के आयामों का उचित नियोजन, 4. क्रियान्वन के लिए अनिवार्य सहयोग जैसे राजनीतिक इच्छाशक्ति, सार्वजनिक व्यय, साझेदारी, भागीदारी, और कार्यपूर्ण करने की दृढ़ता, तथा 5. विभिन्न नीतियों, योजनाओं, कार्यक्रमों और लोगों के मध्य समावेशीकरण।
केंद्र और राज्य सरकारों, स्थानीय प्रशासन, स्वयंसेवी संस्थानों और नागरिक संगठनों द्वारा संचालित कई कार्यक्रम और गतिविधियां (जैसे स्वच्छ भारत मिशन, जल जीवन मिशन, गंगा एक्शन प्लान, यमुना एक्शन प्लान, नेशनल रिवर कन्जर्वेशन प्लान, नमामी गंगे कार्यक्रम, महात्मा गांधी ग्रामीण रोजगार गारंटी कानून, अटल भूजल योजना, अमृत सरोवर, कावेरी कॉलिंग, रैली फॉर रिवर, इत्यादि) हैं, जो नदी पुनर्जीवन से प्रत्यक्ष या अप्रत्यक्ष रूप से संबंधित हैं। नौवीं इंडिया वॉटर इम्पैक्ट समिट का केंद्रीय विषय अतीत से सीखने के उद्देश्य हेतु ऊपर उल्लेखित विभिन्न पहलुओं के अंतर्गत बीते दशकों में नदी पुनर्जीवन और संरक्षण के प्रयासों की प्रभावकारिता का आंकलन करना और भविष्य के लिए रणनीति तैयार करना है।
CITIS – 2025 | Grounding Climate Investment and Technology Innovations at District Level in India
The Climate Investments & Technology Impact Summit (CITIS) represents
a groundbreaking initiative, marking the first event of its kind dedicated to
presenting innovative solutions aimed at generating awareness and accelerating
the uptake of climate action measures. The core philosophy underpinning CITIS
is the recognition that addressing global systemic issues like climate change
necessitates a comprehensive and deep-rooted approach. This approach is
encapsulated in the overarching theme of the conference: “Climate Impact”,
which emphasizes the synergistic integration of three critical components: deep
technology, robust policy, and innovative finance. CITIS will serve as a unique
platform, bringing together disruptive technology companies at the forefront of
climate innovation with influential policy makers and forward- thinking financial
institutions that specialize in providing innovative financial solutions for climate
initiatives.

Grand Challenges
CITIS introduces a format where it presents Grand Challenges that the nation and
the world is facing across 5 thematic sectors. By bringing together experts,
innovators, and decision-makers, CITIS aims to catalyze meaningful progress
towards addressing the urgent and complex challenges posed by climate change,
offering a roadmap for a sustainable and prosperous future.


Poster Exhibition
In addition to its comprehensive discussions and collaborative initiatives, CITIS
will feature a Poster Exhibition, spotlighting disruptive technologies and
innovative solutions that have the potential to revolutionize climate action. This
exhibition will provide attendees with a firsthand look at cutting-edge
innovations and serve as a catalyst for collaboration and knowledge sharing
among stakeholders from various sectors.

Making Solutions Affordable and Accessible
The timing of inaugural CITIS was particularly significant, taking place during
India’s G20 Presidency. This alignment not only underscores the global
importance of the event but also positions India as a leader in the Global South
when it comes to delivering climate solutions that prioritise affordability through
the transformative scale effect. This strategic positioning is poised to have a
resounding impact on the trajectory of climate action within the Global South,
highlighting India’s commitment to fostering sustainable and accessible climate
solutions.
Summit Timetable
-
Day 1
-
Day 2
-
Day 3



Each of the Summits shall have participation of the following key stakeholders:
Indian Government and State Governments
Like every year, the Summit would bring various arms of the Indian Government a central, state and local level together with other national and international stakeholders.
Other Stakeholders
- Country partners
- Industry including technology and engineering companies
- Scientists and technical experts
- Professional services firms
- Investors including family offices, venture capital, private equity and lenders
- Multilateral and Development finance institutions
- Civil society, NGOs and Think-tanks
The Summits are great multi-disciplinary platforms to showcase your efforts, solutions, knowledge through a range of strategic engagement plans. These are:
Strategic Partnerships
This engagement mode is for Government departments at all levels (central, state, municipal), public sector entities, multilateral institutions, NGOs, and foundations who wish to deepen their strategic engagement with India for various environmental programmes. A partnership can entail releasing a special report, initiating a project, highlighting select areas of work or other initiatives.
Sponsorship
For private sector companies or entities wanting brand recognition, the Summits offer a multitude of opportunities including but not limited to hosting networking events, display of special solutions and other showcases. Please get in touch with the Summit team for more details.
Technology and Innovation Showcase
Companies or organizations that have developed solutions, which have the potential of high impact on climate and environment, can get an opportunity to present to stakeholders, potential Indian partners and investors.
Knowledge Partners
Professional service firms and knowledge-oriented institutions are invited to partner with cGanga and NMCG to prepare and launch a number of special reports during the Summits as well as curate and organize the various Summit sessions.
There are various ongoing engagement models that enable partners to find various touch points with the Ganga River Basin. These are:
Working Groups and Task Forces
Interested parties can channel their novel ideas through dedicated task forces and working groups. These groups have in-depth deliberations which are summarized in the form of white papers submitted to Government and various stakeholders. The working groups are a sub-set of 5 major task forces: (i) Science & Research (ii) Engineering & Operations (iii) Technology, Innovation, Entrepreneurship & Skills (iv) Policy, Law & Governance (v) Finance & Investments.
Pilots / Demonstration Projects
Companies interested in introducing their solutions into the River Restoration and Conservation programmes can do so through pilot/demonstration projects. They must however first go through the Environment & Technology Verification (ETV) process. This allows stakeholders to assess the technologies and ascertain value for money.
International Chapters and Roadshows
cGanga and NMCG regularly conduct international roadshows to increase the outreach and awareness. Additionally, countries can establish their own local country chapters to channel their collective innovations and interests into India.
- Participation in the Summit is strictly by invitation only.
- Participants must have a formal invitation from the organizers before attempting registration.
- International participants may register through the following mechanism:
- Their country’s official participation channels.
- Presentation slot in CITIS – subject to prior approval.
- If your nation is not represented formally then kindly send in a formal request so that an invitation may be generated.
- Media partners must be accredited and registered.
- Kindly check www.iwis.cganga.org for more details on or after 20th November 2025.
Registration for your Participation
- All invitations to the Summit shall be issued during 20th November to 05 th December.
- If you have not received the invitation, then please get in touch with the Summit organizers.
The links to the registration process is on through iwis.cganga.org.
Organizer Profiles

National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG)
NMCG is the implementation wing of National Ganga Council which was setup in October 2016 under the River Ganga Authority order 2016. Initially NMCG was registered as a society on 12th August 2011 under the Societies Registration Act 1860. It acted as implementation arm of National Ganga River Basin Authority (NGRBA) which was constituted under the provisions of the Environment (Protection) Act (EPA) 1986. NGRBA has since been dissolved with effect from the 7th October 2016, consequent to constitution of National Council for Rejuvenation, Protection and Management of River Ganga (referred to as National Ganga Council). NMCG is under the aegis of Ministry of Jal Shakti, Government of India.

Centre for Ganga River Basin Management and Studies
Centre for Ganga River Basin Management and Studies (cGanga)
cGanga is a think tank and a centre of excellence formed under the aegis of NMCG, and one of its stated objectives is to make India a world leader in river and water science. The Centre is headquartered at IIT Kanpur and has representation from most leading science and technological institutes of the country. cGanga’s mandate is to serve as think-tank in implementation and dynamic evolution of Ganga River Basin Management Plan (GRBMP) prepared by the Consortium of 7 IITs. In addition to this it is also responsible for introducing new technologies and innovations as well as novel policy, governance and financial solutions for the water sector in India.

NRCD
National River Conservation Directorate D/O WR, RD & GR Ministry of Jal Shakti
National River Conservation Directorate (NRCD)
The National River Conservation Directorate, functioning under the Department of Water Resources, River Development & Ganga Rejuvenation, and Ministry of Jal Shakti providing financial assistance to the State Government for conservation of rivers under the Centrally Sponsored Schemes of ‘National River Conservation Plan (NRCP)’. www.nrcd.nic.inCentres for Six River Basin Management Studies
The Centres for six River Basin Management Studies are Brain Trusts dedicated to River Science and River Basin Management, established in 2024 by 12 technical Institutions (IITs, NITs and NEERI), under the leadership of cGanga at IIT Kanpur. The centres serve as knowledge wing of the National River Conservation Directorate (NRCD) under the Ministry of Jal Shakti.
The vision for these centres was laid out in 2019 by the President of India, who emphasized the need for comprehensive management of six major river basins, akin to the work done for the Ganga basin. The goal is to study these basins, assess their status, and develop strategies for restoration and sustainable management.
Condition Assessment and Management Plan (CAMP) studies of each of the six river basins have been assigned to specific institutions with expertise in their unique geographical, ecological, and hydrological characteristics.
These centres are committed to restoring and conserving the six major rivers and its resources through the collation of information and knowledge, research and development, planning, monitoring, education, advocacy, and stakeholder engagement.
Panelists
Plenary














Science and Policy










































Finance and Economics

Technology & Innovation












International



Implementation and challenges







Member Institutions














Summit Partners
The organisers are grateful to all supporting partners for their contribution in making this event possible.

Samarth Ganga Foundation is a new entity and a strategic collaborator to cGanga. Designed as an “applied innovation and impact” think- tank, the non-profit entity specialises in developing solutions with high economic impact. SGF is supporting cGanga to advocate the solution across the nation to various urban local bodies.

The Bharat Technology & Impact Accelerator (BHARATIA) specialises in technology commercialisation by bringing disruptive innovation from around the world to India. BHARATIA is a SGF initiative.

The India Water Leaders’ Council is composed of senior representation from various stakeholders of the water industry ecosystem in India. The IWLC meets once per quarter to discuss and debate critical issues and how to address those. IWLC stands firmly behind the decentralised waste-water treatment.
ETV Participants






















Previous Summits
7th IWIS 2022 :The Convergence of 5Ps : People, Policies, Plans, Programmes, and Projects.
8th IWIS 2023 :The convergence
of deep technology, rigorous policy frameworks.
9th IWIS 2024 :The convergence achieved,
we identified seven or eight key take aways that will be published.
Recently Released Reports
Pragyambu
(cGanga Quarterly Digest)
Engage With Us
A. Engagement Models during the Summit
- Strategic Partnerships
- Sponsorship
- Technology and Innovation Showcase
- Knowledge Partners
Professional Service Firms and Knowledge-oriented institutions are invited to partner with cGanga and NMCG to prepare and launch a number of special reports during the Summit as well as curate and organise the various Summit sessions.
B. Ongoing Engagement Models
- Working Groups and Task Forces
- Pilots / Demonstration Projects
- International Chapters and Roadshows
Contact Details
General Enquiries and Submissions of Participation Requests:
For Indian Government Related Queries:
Dr Vinod Tare: vinod.tare@cganga.org
For International Participation and Summit Partnerships:
Mr Sanmit Ahuja: sanmit.ahuja@cganga.org





















































